One Dimension Collision JS Model
The motion of a body of mass m and velocity v is described by a vector quantity known as momentum p where
The total momentum of a system remains constant provided that no external resultant force acts on the system.
For two bodies colliding linearly, it is written mathematically as a vector equation
Total initial momentum = total final momentum
Collisions can be generally classified into these categories:
- perfectly inelastic, e= 0
- inelastic, e is a value from 0 to 1
- perfectly elastic, e=1
There is also a concept of kinetic energy of a moving body is stated mathematically by the following equation:
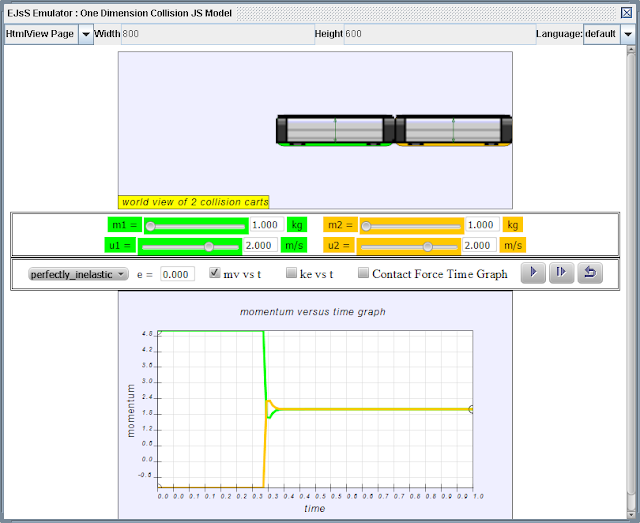
Main Simulation View
The simulation has 2 collision carts on friction-less floor.Sliders
Explore the sliders allows varying the variables .
- mass of cart ONE, mass_1, m1 in kg
- initial velocity of cart ONE, u1 in m/s
- mass of cart TWO, mass_2, m2 in kg
- initial velocity of cart TWO, u2 in m/s
Drop Down Menu
Allows for selecting what kind of collision is simulated.A Perfectly elastic collision is defined as one in which both conservation of momentum and conservation of kinetic energy are observed
A Perfectly Inelastic collision is defined as one in which conservation of momentum is observed but the colliding carts stick together after collision with kinetic energy loss
Checkboxes
Shows the Contact Force versus Time graphButtons
PlayStep Back
Reset
have their usual meaning.
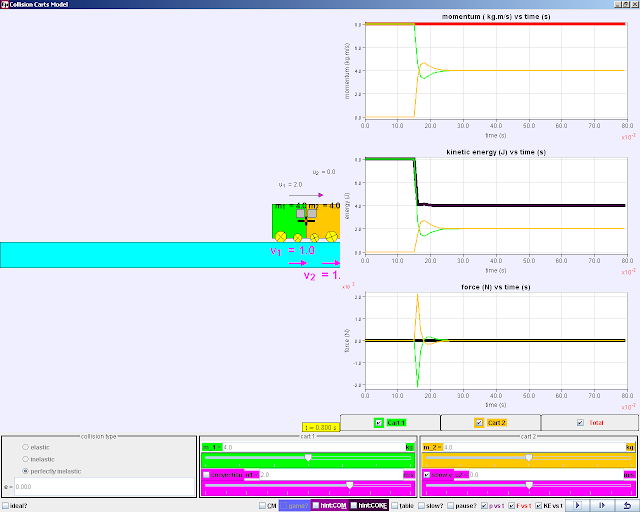
A more powerful version of this simulation is available here
is available on the NTNU website http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=831.0
or here
Shout our thanks to the Ejs community namely, Francisco Esquembre , Fu-Kwun Hwang and Wolfgang Christian for their professional learning community support.