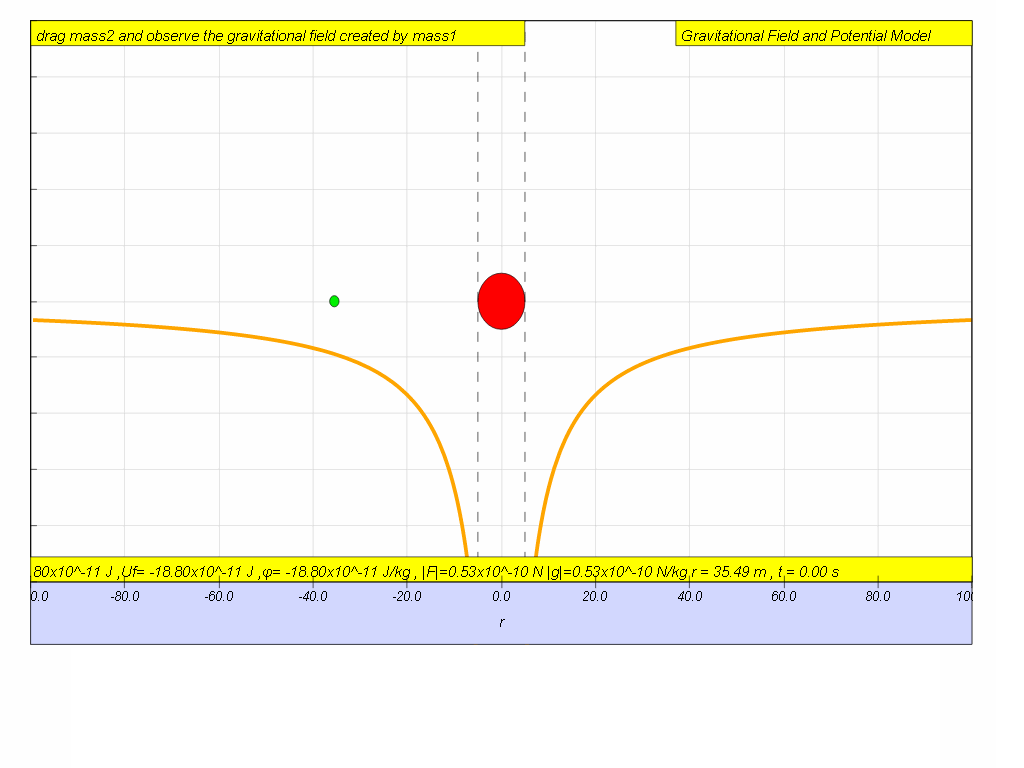
Gravitational
Potential (symbol: φ and units: J kg-1)
The gravitational potential, φ , at a point due to the
gravitational field set up by a mass M is defined as the work done per unit
mass in bringing a point mass from infinity to that point.
Mathematically,
it can be shown that
Note:
1) This expression is similar to the expression for
gravitational potential energy, . and they are related by U = mφ.
2) Gravitational
potential is a scalar quantity. (i.e. it has no direction and a
negative value simply means it is less than zero).
3) This expression
implies that φ is also always negative (less than zero) and by
convention, the gravitational potential at infinity is also taken
to be zero (maximum).
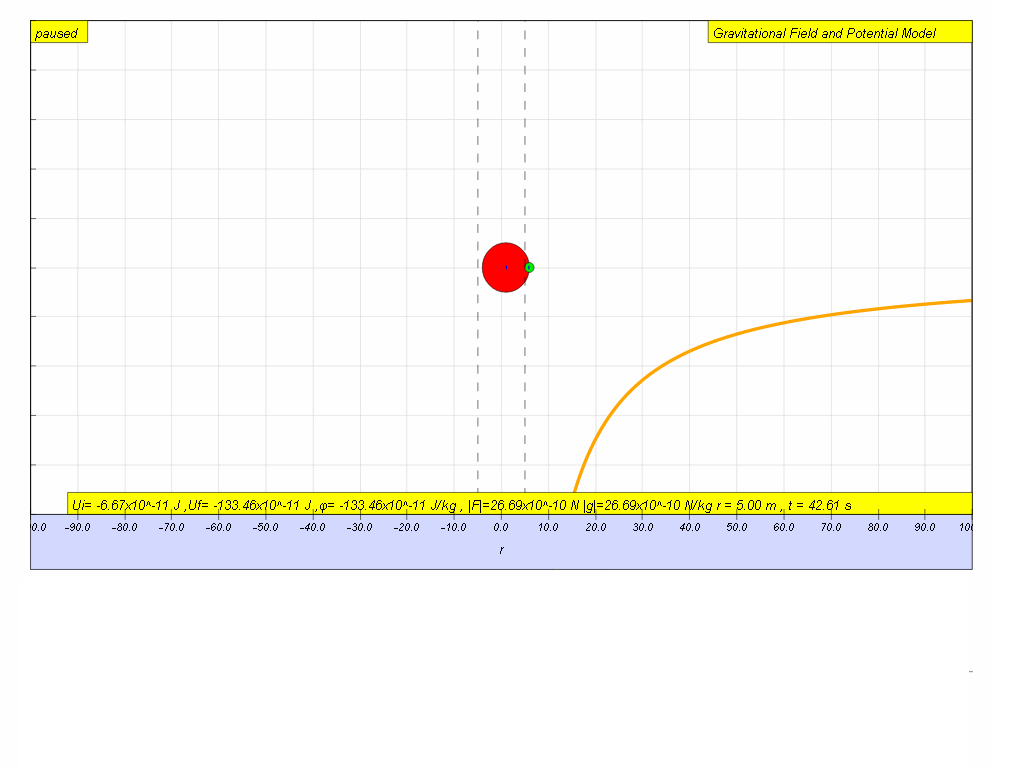
4) Similar to
gravitational field strength , gravitational potential is also independent of the mass of the
point mass, m.
5) As distance r of
the point mass from source mass increases, φ increases according
to the equation .
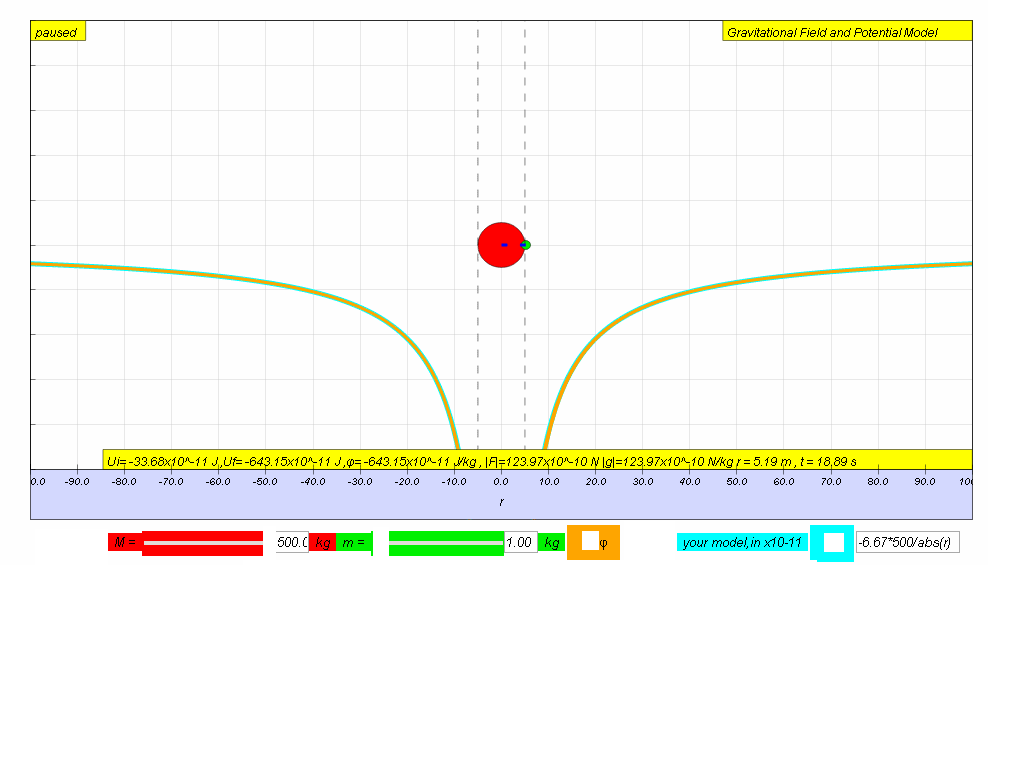
Try to input your own model for
potential until you achieve a close fit to the data set graph from
potential.
hint:
What is the value of M is the model?
no need to key in x10-11
abs in java is absolute | |
that always make the value positive.
try something like -6.67*500/abs(r) in
the equivalent for
Summary
| symbol |
g |
φ |
| name |
Field strength |
Potential |
| units |
N kg-1 or m s-2 |
J kg-1 |
| meaning |
Force per unit mass |
Potential energy per unit mass |
| quantity |
vector |
scalar |
| equation |
towards
the centre of the source mass
|
|
| relationship to mass |
Force, =
mg |
Potential energy, =
mφ |
| graph |
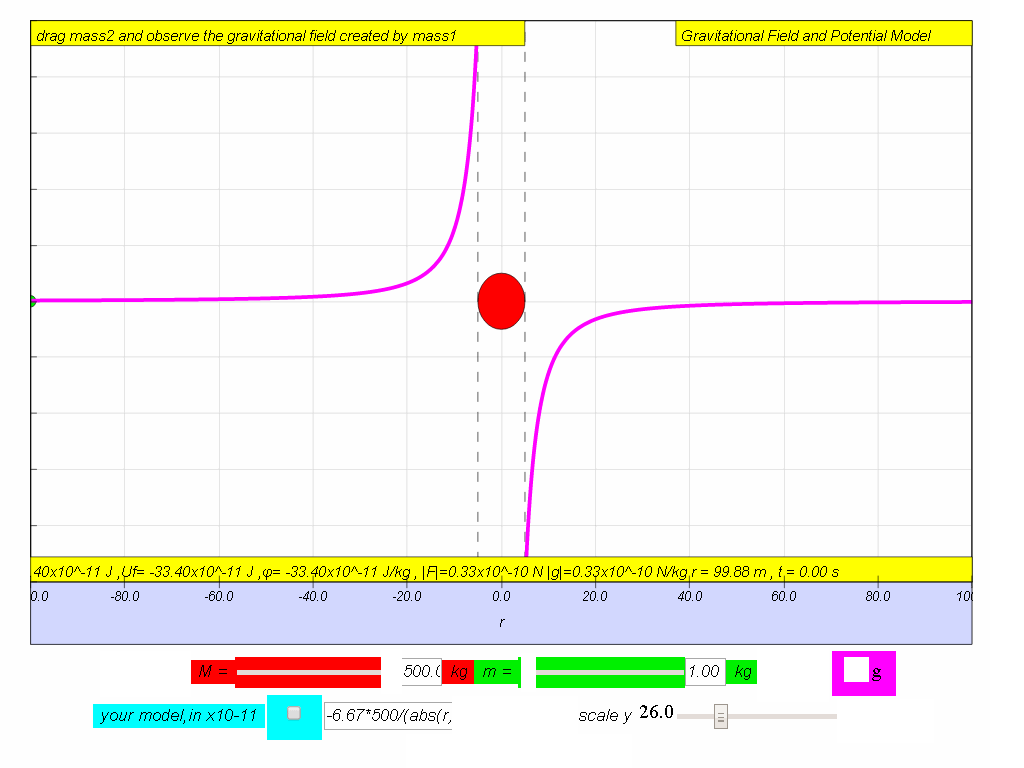
|
 |
| computer model if M = 500. |
-6.67*500/(abs(r)*r) |
-6.67*500/abs(r) |
Model
https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/44365627/lookangEJSworkspace/export/ejss_model_gravity06/gravity06_Simulation.xhtml






