
About
For Teachers
- 88.mp4
- 88-frame.mp4
- 88-frame.gif
Software Requirements
| Android | iOS | Windows | MacOS | |
| with best with | no | no | need Java |
need Java |
| support full-screen? | no | no | Yes | Yes |
| cannot work on | no mobile browser understand Java.... |
no mobile browser understand Java.... | install Tracker from http://physlets.org/tracker/ |
install Tracker from http://physlets.org/tracker/ |
Credits
end faq
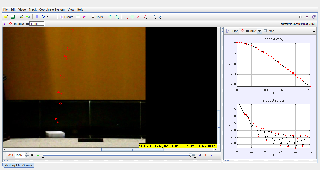
Theory
the equation for the drag force on the square paper is may be assumed to be is the form of \( F = \frac{1}{2} \rho v^{2} C_{D} A \)
where F is the aerodynamic drag force
\( \rho \) is the is the density of the fluid
\( v \) is the speed of the object relative to the fluid
\( A \) is the cross sectional area
\( C_{D} \) is the drag coefficient – a dimensionless number.
Data
| Area, A/ \( cm^{2} \) | 289 | 249 | 190 | 169 | 130 | 88 |
| Terminal Velocity, v/ \( cms^{-1} \) | 1.66 | 1.70 | 2.02 | 2.12 | 2.31 | 2.66 |
Version
http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2016/08/sypt2016-workshop-materials.html
end faq
Facebook Social Comments
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 02 Newtonian Mechanics
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 4292

