About
1.7 Forced Oscillations and Resonance LO (j)
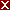
When a system performs oscillations without any applied force, the frequency of the oscillation is a characteristic of the system and is called the natural frequency, fo . In the example above, the fo = 0.161 Hz.
1.7.1 Spring Mass System initially at Rest
Consider a spring mass system initially at rest.
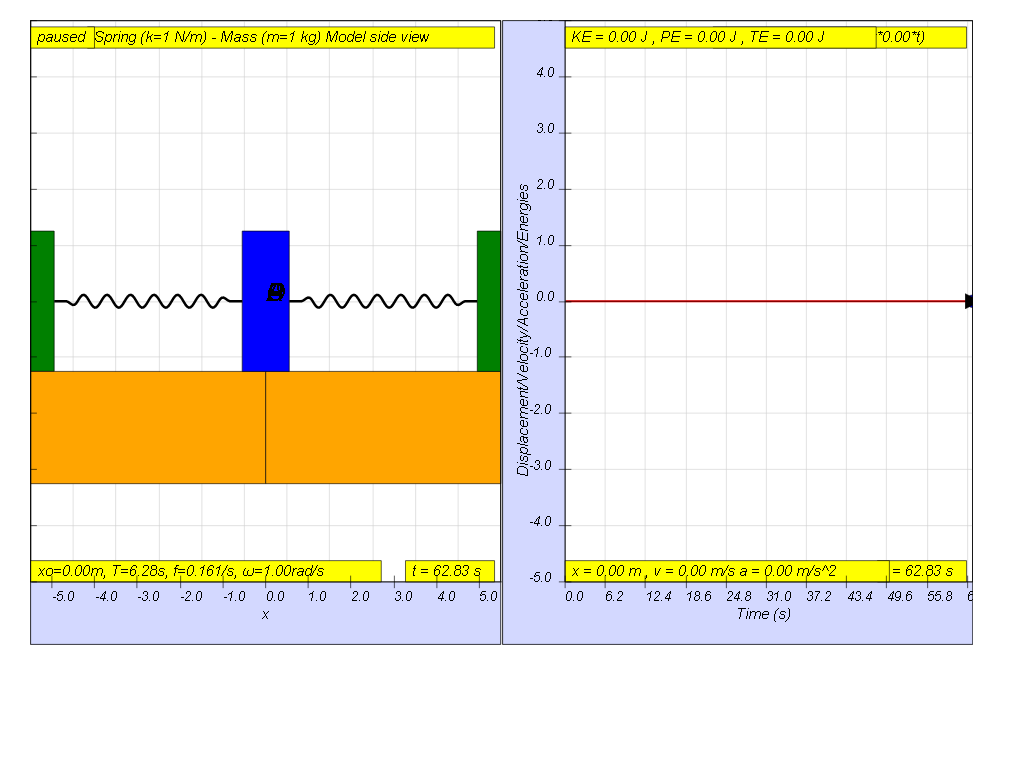
1.7.1.1 No driving force
When the driving force is at f = 0, that means the driving force is Fdriver = (0.5)sin(2π f t ) = 0.
the result is as shown on the picture where x = 0 for all time since there is no external driving force acting on the system.
1.7.1.2 Slow driving force
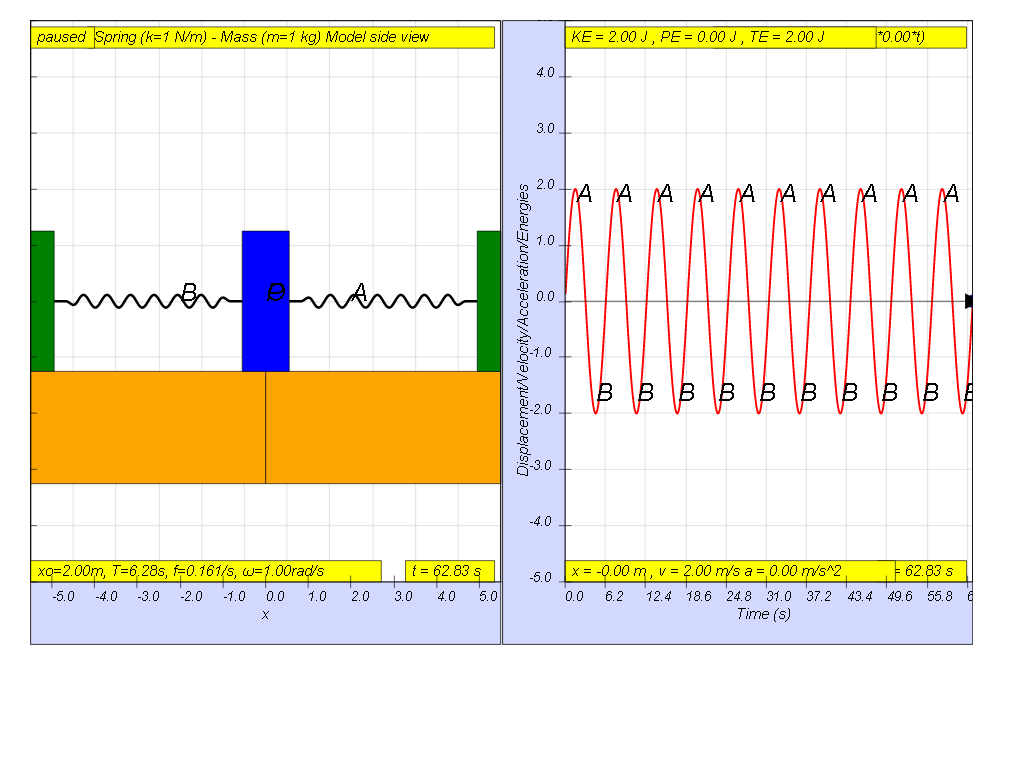
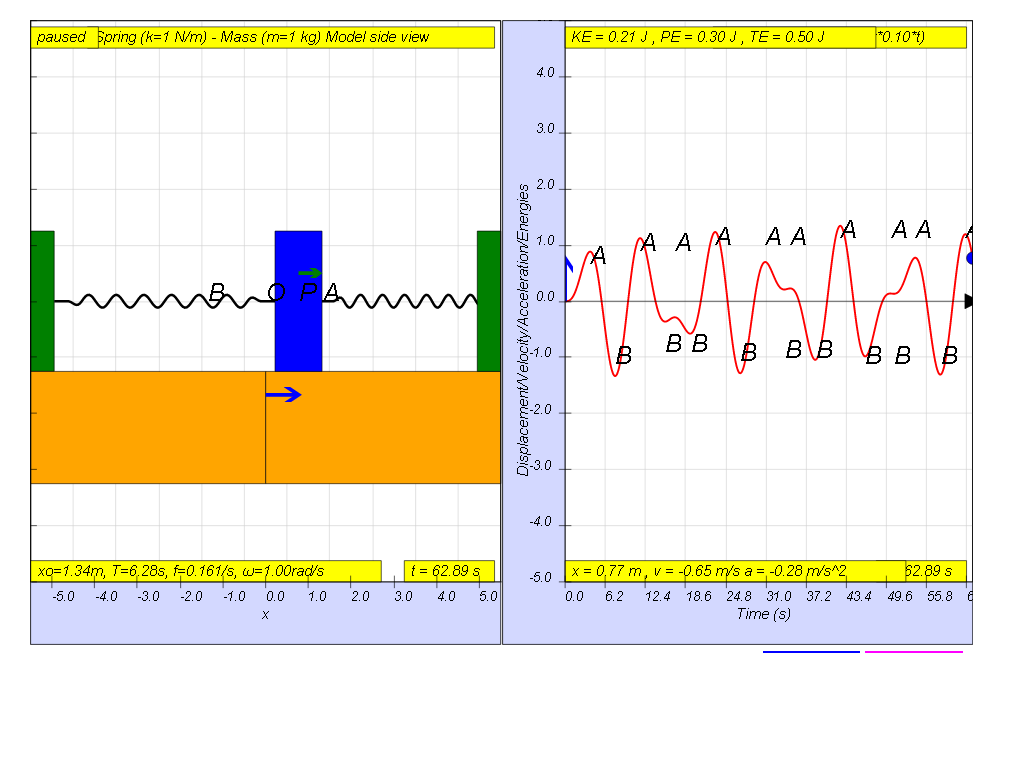
However, when f = 0.1 , the Fdriver = (0.5)sin(2π (0.1) t ), it results in a motion that seems to irregular reaching a maximum amplitude of A and B (see picture).
1.7.1.3 Driving force equal Natural frequency
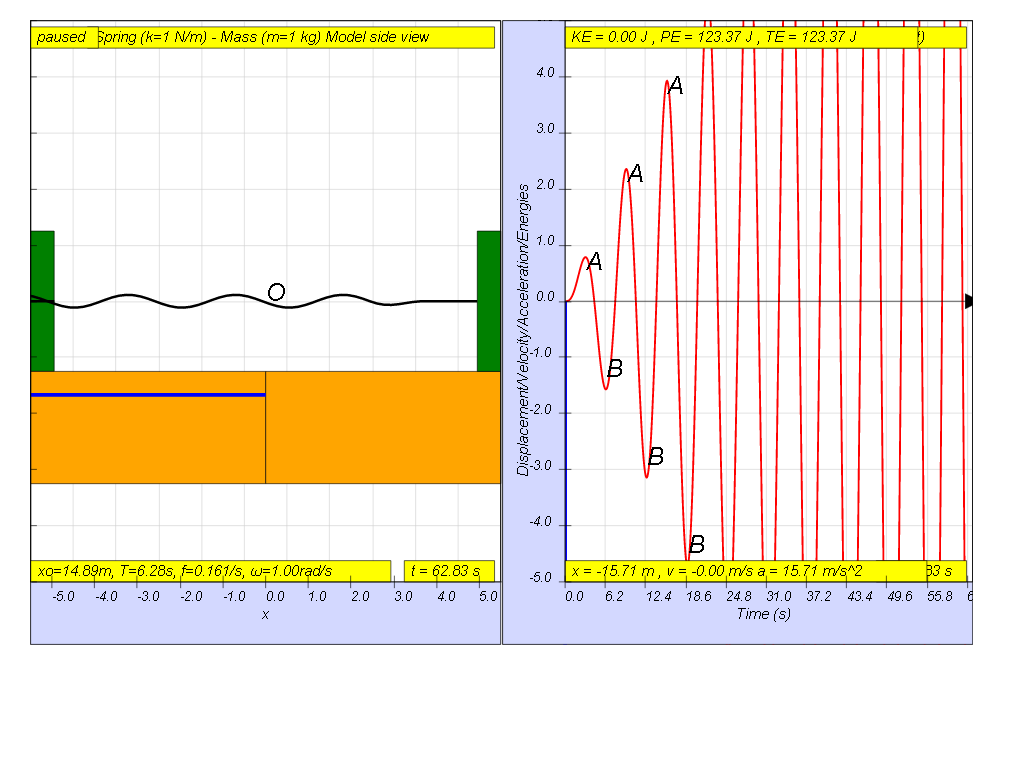
However, when f = 0.159 , the Fdriver = (0.5)sin(2π (0.159) t ), it results in a motion that seems to increase to a very large maximum amplitude of A and B (see picture, when t = 55.8, A and B are greater than the screen display height). Theoretically, is should be infinitely large.
1.7.1.4 Driving force greater than Natural frequency
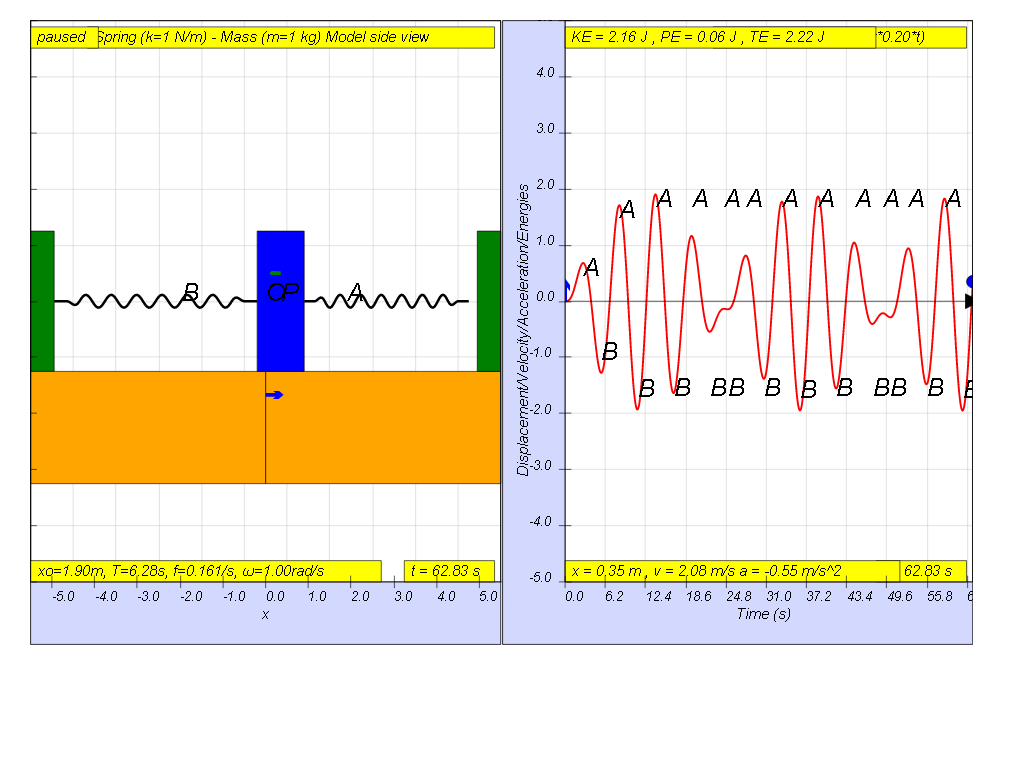
However, when f = 0.2 , the Fdriver = (0.5)sin(2π (0.2) t ), it results in a motion that seems to also reach some smaller maximum amplitude of A and B (see picture reaching about 1.8 ).
1.7.1.5 Driving force much greater than Natural frequency
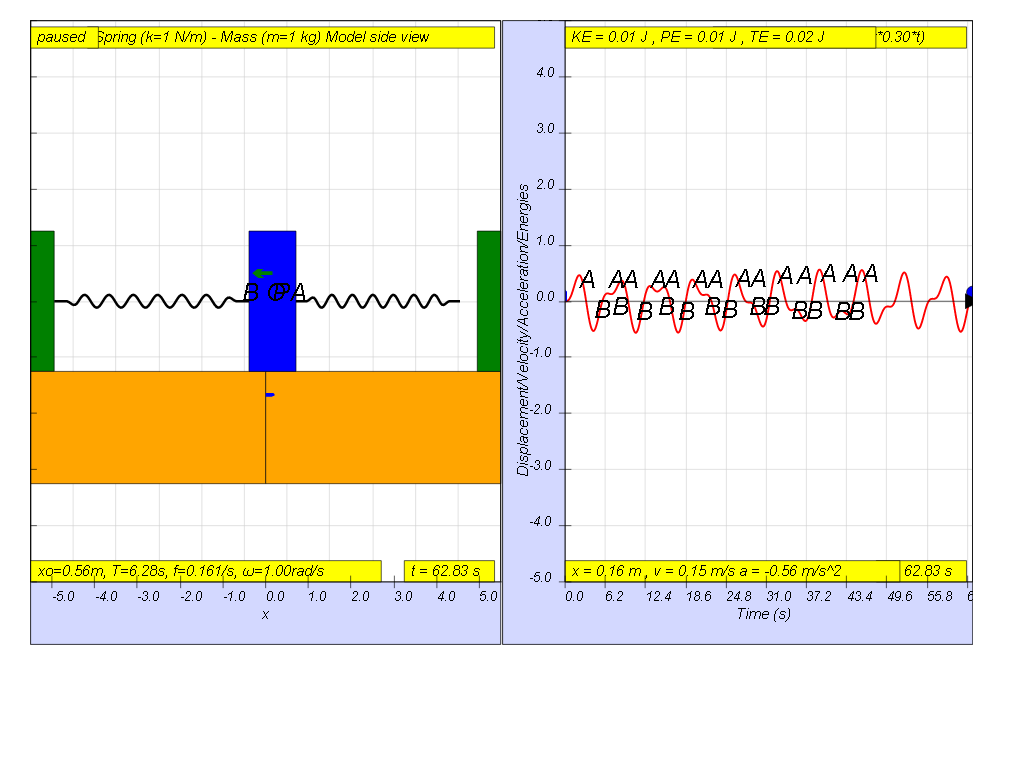
However, when f = 0.3 , the Fdriver = (0.5)sin(2π (0.3) t ), it results in a motion that seems to also reach rather maximum amplitude of A and B (see picture reaching about 0.5 ).
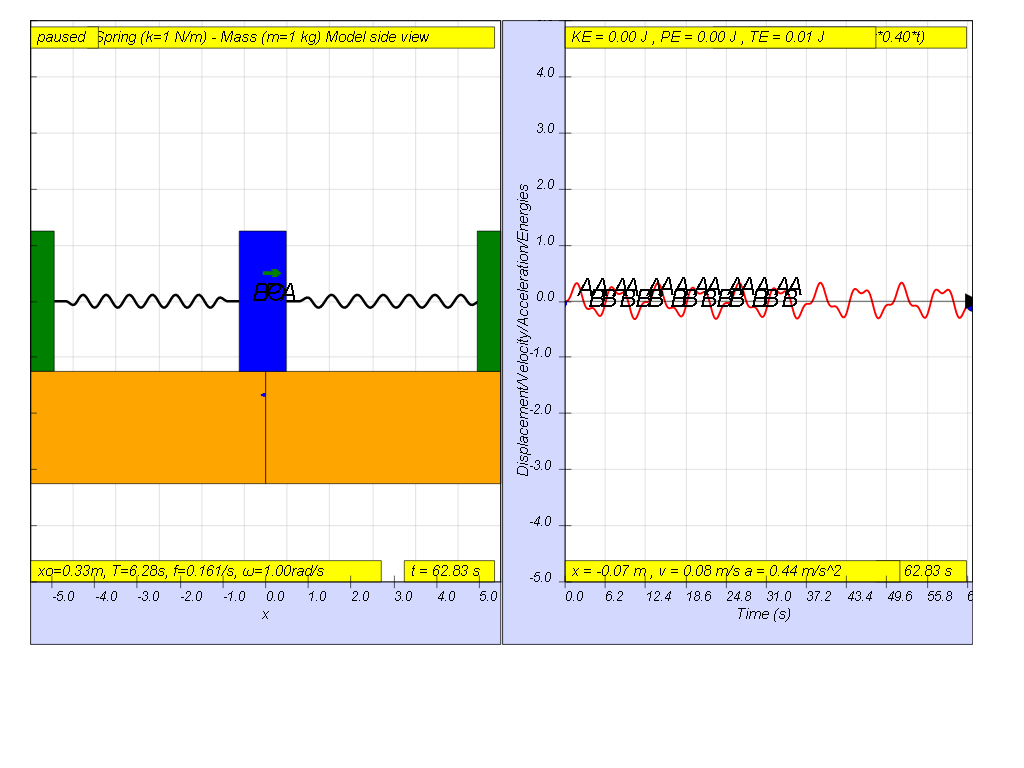
Lastly, when f = 0.4 , the Fdriver = (0.5)sin(2π (0.4) t ), it results in a motion that seems to also reach even smaller maximum amplitude of A and B (see picture reaching about 0.3 ).
These oscillations in which a periodic force is imposed are called forced resonance. Systems will then some what influenced to vibrate at the frequency of the periodic force, f, but only when f = fo = 0.161 Hz , in this example, the maximum amplitude is the greatest happens in this case when damping is zero as has similar maximum amplitude effects for different damping levels occurring near f = fo
1.7.2 Examples include the
1) Vibrations of a pendulum clock.
2) Vibrations of a tuning fork when exposed to the periodic force of a sound wave.
3) Vibration of a bridge under the influence of marching soldiers or periodic wind.
1.7.3 Model:
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Software Requirements
| Android | iOS | Windows | MacOS | |
| with best with | Chrome | Chrome | Chrome | Chrome |
| support full-screen? | Yes. Chrome/Opera No. Firefox/ Samsung Internet | Not yet | Yes | Yes |
| cannot work on | some mobile browser that don't understand JavaScript such as..... | cannot work on Internet Explorer 9 and below |
Credits
 This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
end faq
Apps
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ionicframework.shm23app540489&hl=en
end faq
Testimonials (0)
There are no testimonials available for viewing. Login to deploy the article and be the first to submit your review!
You have to login first to see this stats.